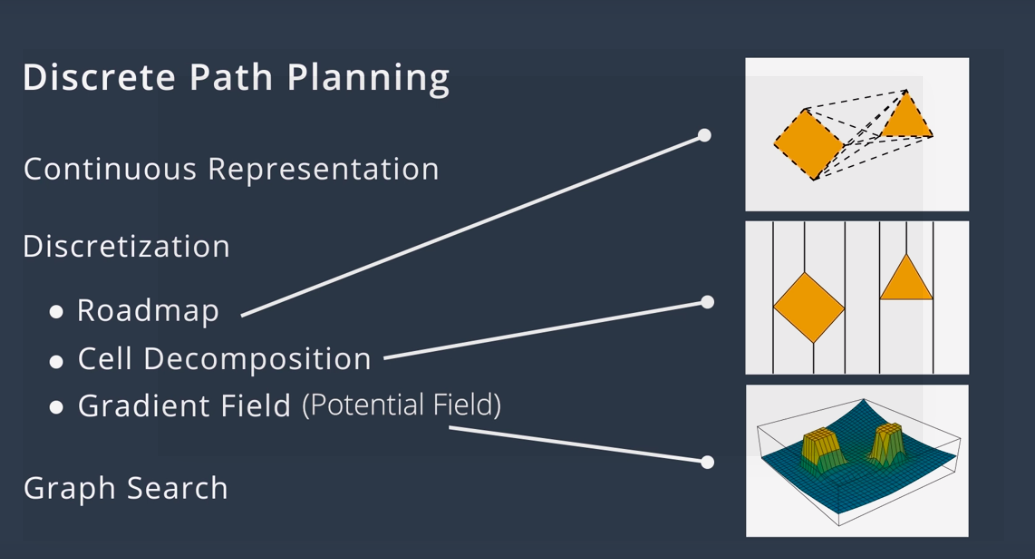
Discrete Planning
Discrete planning looks to explicitly discretize the robot's workspace into a connected graph, and apply a graph-search algorithm to calculate the best path. This procedure is very precise (in fact, the precision can be adjusted explicitly by changing how fine you choose to discretize the space) and very thorough, as its discretizes the complete workspace. As a result, discrete planning can be very computationally expensive - possibly prohibitively so for large path planning problems.
The image below displays one possible implementation of discrete path planning applied to a 2-dimensional workspace.
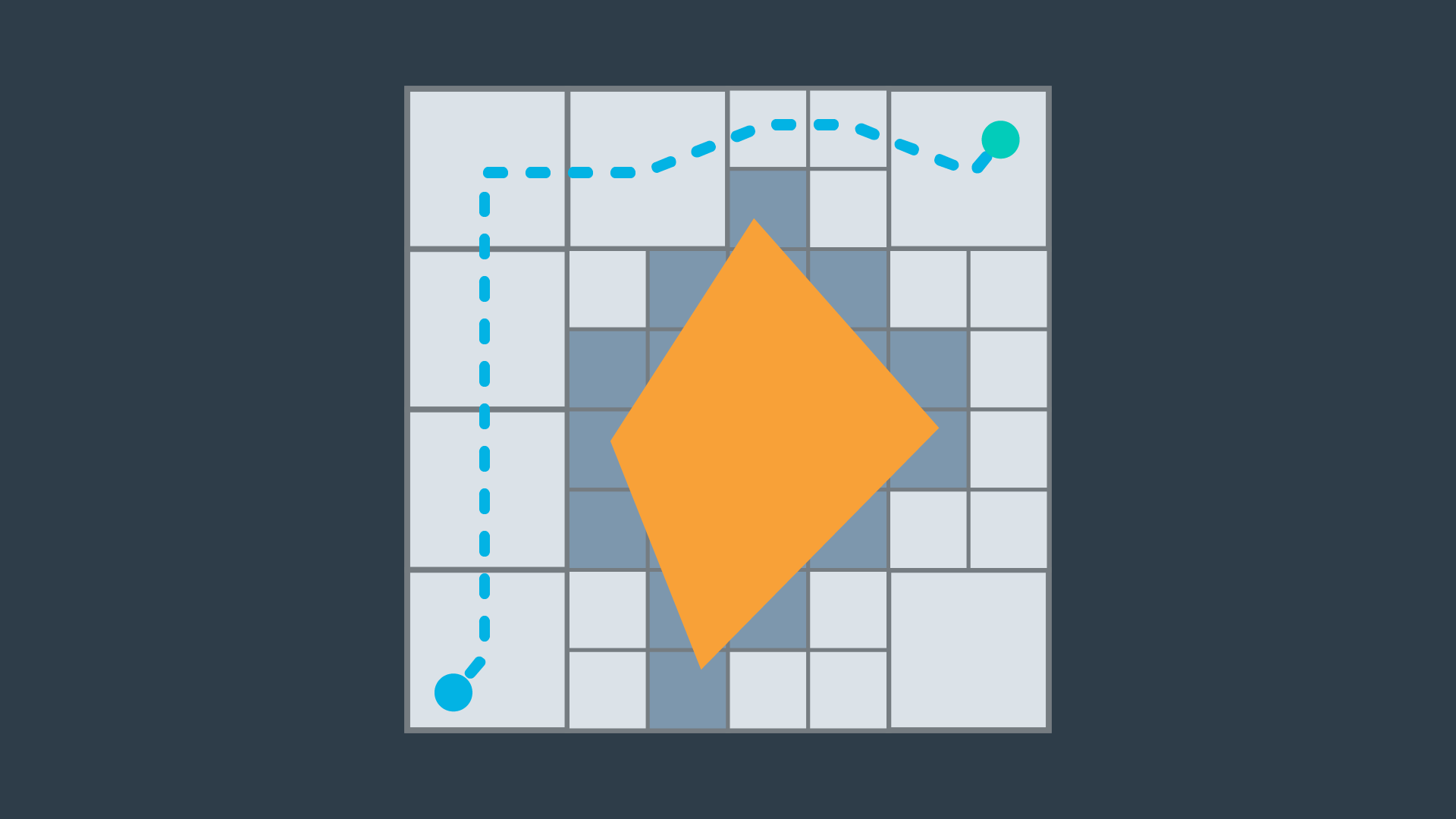
Discrete path planning is elegant in its preciseness, but is best suited for low-dimensional problems. For high-dimensional problems, sample-based path planning is a more appropriate approach.